On This Page:
- Background
- Measure
- Healthy People 2030 Target
- Data Source
- Trends and Most Recent Estimates
- Additional Information
In 2022 to 2023, 32.3% of adults aged 18 years and older who smoke or smoked and attempted to quit in the past year used a smoking cessation treatment in the quit attempt.
Background
Quitting smoking has major and immediate health benefits for people of all ages. It dramatically reduces the risk of lung and other cancers caused by smoking, as well as the risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Cessation success is increased by the use of evidence-based treatment, including the use of behavioral counseling and medications. The combination of behavioral counseling and medication is especially effective. FDA-approved cessation medications include various forms of nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), and two medications that do not contain nicotine: bupropion (also known as Zyban), and varenicline (also known as Chantix). Behavioral support can be delivered in person, in group settings, over the phone (quitlines and telehealth sessions), and with other mobile technology tools and methods (i.e., mHealth). However, few people who smoke use evidence-based cessation treatments when attempting to quit, which decreases their likelihood of success.
E-cigarettes (also known as vapes or Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems) are battery-powered devices that convert a liquid (“e-liquid”) into an aerosol. E-liquids typically contain nicotine, flavorings, vegetable glycerin, propylene glycol and other chemicals. In addition to nicotine, e-cigarette aerosol may contain heavy metals, volatile organic compounds, and fine and ultrafine particles that can be inhaled deeply into the lungs by both users and bystanders. Many people who smoke report using e-cigarettes in an effort to quit smoking. However, the Surgeon General has concluded that there is presently inadequate evidence to conclude that e-cigarettes, in general, increase smoking cessation, and no e-cigarette has been approved by FDA as a therapeutic product for smoking cessation treatment.
Measure
The three measures presented here (“Any Cessation Treatment,” “Any Cessation Medication,” and “Any Cessation Counseling”) use a common denominator consisting of adults (age 18 years and older) who smoke at the time of interview and report a quit attempt during the past 12 months as well as adults who formerly smoked but quit smoking within the past 12 months. The numerators for each measure consist of adults reporting the following behaviors:
Any Cessation Medication Use: adults who reported using any NRT(s) (patch, gum, lozenge, nasal spray or oral inhaler) and/or reported using any of the following medications: Bupropion (Zyban®) and/or Varenicline (Chantix®).
Any Cessation Counseling Use: adults who reported using any of the following type(s) of behavioral counseling: from a quit-line; one-on-one with a clinician; at a clinic, class or support group; or from the internet (i.e., web-based), a smartphone app, or a texting program. (Note: The 2020 Surgeon General’s Report on Smoking Cessation concluded that evidence is inadequate to infer that smartphone apps for smoking cessation are independently effective in increasing smoking cessation.)
Any Cessation Treatment Use: adults who reported using one or more of the cessation medications and/or cessation counseling types included in the above two measures.
Data Source
National Cancer Institute. Tobacco Use Supplement to the Current Population Survey.
Healthy People 2030 Target
- Healthy People 2030 includes a goal to increase the use of smoking cessation counseling and medication in adults who smoke (TU-13) which relies on National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data. In 2022, 38.4 percent of adults who smoke and who tried to quit during the past year (and adults who formerly smoked and who quit during the past 2 years) reported using cessation counseling and/or medication as part of a quit attempt. The 2030 target for this goal is 43.8%. In contrast, the data presented in the Cancer Trends Progress Report are drawn from the Tobacco Use Supplement to the Current Population Survey (TUS-CPS). Therefore, the data presented in this report cannot be directly compared to the HP2030 objective.
Healthy People 2030 is a set of goals set forth by the Department of Health and Human Services.
Trends and Most Recent Estimates
- Any Cessation Treatment
Percentage of adults aged 18 years and older who smoke or smoked and used a smoking cessation treatment (counseling and/or medication) in an attempt to quit smoking in the past year, 2003-2023 Overview Graph Detailed Trend Graphs Most Recent Estimates (2022 to 2023) Percent 95% Confidence Interval 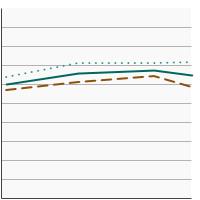

Both Sexes 
32.3 30.7 - 33.9 Male 
29.3 27.3 - 31.4 Female 
35.8 33.2 - 38.4 - Cessation Medication
Percentage of adults aged 18 years and older who smoke or smoked and used a smoking cessation medication in an attempt to quit smoking in the past year, 2003-2023 Overview Graph Detailed Trend Graphs Most Recent Estimates (2022 to 2023) Percent 95% Confidence Interval 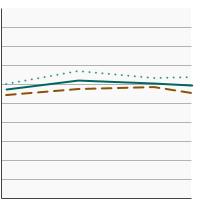

Both Sexes 
29.7 28.2 - 31.2 Male 
27.7 25.8 - 29.6 Female 
31.8 29.4 - 34.3 - Cessation Counseling
Percentage of adults aged 18 years and older who smoke or smoked and used smoking cessation counseling in an attempt to quit smoking in the past year, 2003-2023 Overview Graph Detailed Trend Graphs Most Recent Estimates (2022 to 2023) Percent 95% Confidence Interval 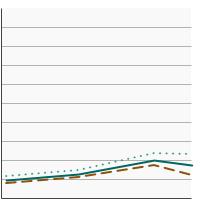

Both Sexes 
8.6 7.7 - 9.6 Male 
6.1 5.1 - 7.3 Female 
11.5 9.9 - 13.3
Additional Information
- Cigarette Smoking: Health Risks and How to Quit (PDQ®)–Patient Version. National Cancer Institute.
- What You Need to Know About Quitting Smoking. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
- Adult Smoking Cessation – The Use of E-Cigarettes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Quitting Resources
- How To Quit. Smokefree.gov.
- Where To Get Help When You Decide To Quit Smoking. National Cancer Institute.
- Tips for Coping with Nicotine Withdrawal and Triggers. National Cancer Institute.
- How to Quit Smoking. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Want to Quit Smoking? FDA-Approved Products Can Help. U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
- Smoking Cessation: A Report of the Surgeon General. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Treatment of Tobacco Smoking: A Review. JAMA Network.
- Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 Update. US Department of Health and Human Services.
- CPSTF Finding and Rationale Statement - Tobacco Use: Mobile Phone Text Messaging Interventions for Smoking Cessation. Community Preventive Services Task Force
- Tobacco Use: Internet-based Interventions to Increase Tobacco Use Cessation. Community Preventive Services Task Force
- Best Practices User Guide: Cessation in Tobacco Prevention and Control. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Effectiveness of Very Brief Advice on Tobacco Cessation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cheng CC, He WJ, Gouda H, Zhang MJ, Luk TT, Wang MP, Lam TH, Chan SS, Cheung YT. J Gen Internal Med. 2024 May 2:1-4.
- The effectiveness of smartphone app–based interventions for assisting smoking cessation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Guo YQ, Chen Y, Dabbs AD, Wu Y. J Med Internet Res. 2023;25:e43242.
- Antidepressants for smoking cessation. Hajizadeh A, Howes S, Theodoulou A, Klemperer E, Hartmann-Boyce J, Livingstone-Banks J, Lindson N. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023(5).
- Systematic review of psychosocial smoking cessation interventions for people with serious mental illness. Hawes MR, Roth KB, Cabassa LJ. J Dual Diagn. 2021 Jul 3;17(3):216-35.
- Effectiveness of smoking cessation interventions among adults: an overview of systematic reviews. Systematic Reviews. Hersi M, Beck A, Hamel C, Esmaeilisaraji L, Pussegoda K, Austin B, Ahmadzai N, Pratt M, Thuku M, Yazdi F, Bennett A. Syst Rev. 2024;13(1):179.
- Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation. Lindson N, Butler AR, McRobbie H, Bullen C, Hajek P, Begh R, Theodoulou A, Notley C, Rigotti NA, Turner T, Livingstone-Banks J. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024(1).
- What Are the Effective Components of Group-Based Treatment Programs For Smoking Cessation? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mersha AG, Bryant J, Rahman T, McGuffog R, Maddox R, Kennedy M. Nicotine Tob Res. 2023;25(9):1525-37.
- Assessment of Racial Differences in Pharmacotherapy Efficacy for Smoking Cessation: Secondary Analysis of the EAGLES Randomized Clinical Trial. Nollen NL, Ahluwalia JS, Sanderson Cox L, et al. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jan 4;4(1):e2032053.
- Different doses, durations and modes of delivery of nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation. Theodoulou A, Chepkin SC, Ye W, Fanshawe TR, Bullen C, Hartmann-Boyce J, Livingstone-Banks J, Hajizadeh A, Lindson N. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023(6).
- Smoking-Cessation Interventions for U.S. Young Adults: Updated Systematic Review. Villanti AC, West JC, Klemperer EM, et al. Am J Prev Med. 2020;59(1):123-136.
- Efficacy and safety of pharmacological intervention for smoking cessation in smokers with diseases: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Xing X, Shang X, Deng X, Guo K, Fenfen E, Zhou L, Wang Y, Yang C, Yang K, Li X. J Evid Based Med. 2023;16(4):520-33.
- Effectiveness of peer-support interventions for smoking cessation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Yuan P, Westmaas JL, Thrul J, Toussaert S, Hilton JF, White JS. Nicotine Tob Res. 2023;25(9):1515-24.